Application Performance Optimization : Materialized Views
Mohammad Al-Jundi
Senior System Engineer @ Innotech
Content
- Caching & how it works.
- Caching Pros & Cons.
- Materialized Views.
- When we can use Materialized Views.
- Similarities & Differences.
- Materialized Views scenario and examples
Caching
- Caching is a cost-effective solution that ensures fast response for most businesses.
- Caching is used to store two main types of data:
- Frequently used data.
- Data need more computations and calculations
How does caching work
- The data in a cache is generally stored in fast access hardware such as RAM.
- A cache's primary purpose is to increase data retrieval performance by reducing the need to access the underlying slower storage layer.
- Caches can be applied throughout various layers of technology including Operating Systems, Networking layers including Content Delivery Networks (CDN) and DNS, web applications, and Databases.
Caching Pros & Cons
-
Pros:
- Better speed.
- Reduce bottleneck.
-
Cons:
- Small size.
- Expensive.
- Need to be recalculated.
Materialized Views
- A materialized view is a database object that contains the results of a query for later use.
- Materialized views can speed up expensive aggregation, and selection operations, especially those that run frequently and that run on large data sets
Deciding When to Create a Materialized View
Materialized views are particularly useful when:- Query results contain a small number of rows and/or columns relative to the base table.
- Query results contain results that require significant processing, aggregates that take a long time to calculate.
- The view’s base table does not change frequently.
A Materialized View or a Regular View ?
Create a materialized view when all of the following are true:
- The Query results from the view don’t change often.
- The Results of the view are used often.
- The Query consumes a lot of resources.
A Materialized View or a Regular View ?
Create a regular view when any of the following are true:
- The Results of the view change often.
- The Results are not used often.
- The Query is not resource intensive so it is not costly to re-run it.
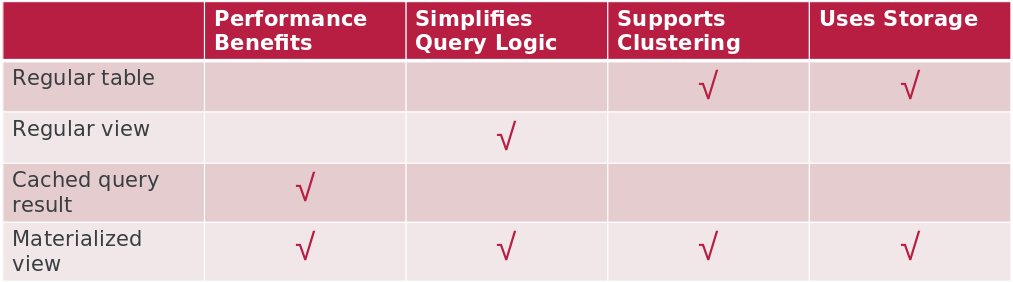
Similarities and Differences
Some Use Cases
- Real life scenario - Central pharmacy stock.
- Real life scenario - Aggergate Sales Statistics
- Real life scenario - multi-currency e-store items
- General scenario - Query Q contains an expensive sub-query S
Thank You
